Computer crashes can be frustrating, especially when they happen frequently without an obvious cause. One powerful but often overlooked tool in Windows is System Configuration, also known by its executable name, msconfig.
This utility allows users to diagnose and isolate issues that could be causing system instability, startup errors, or application crashes. When used properly, msconfig can help track down the root of crashes without needing deep technical knowledge.
What Is System Configuration (msconfig)?
System Configuration is a built-in Windows utility that allows users to:
- Control which programs and services load during startup
- Switch between normal and diagnostic startup modes
- Boot into Safe Mode or other advanced startup environments
- Enable or disable system services and drivers
Because many crashes stem from software conflicts, outdated drivers, or problematic startup items, msconfig is ideal for methodically narrowing down the causes.
When to Use msconfig for Troubleshooting
You should consider using msconfig when you encounter any of the following:
- Frequent system crashes without a clear trigger
- Blue screen errors (BSOD) that occur at startup
- Applications that crash immediately upon opening
- Sudden system freezes
- Unusually long boot times
Msconfig does not fix crashes directly but is essential for isolating problematic software or services that might be the underlying cause.
Accessing System Configuration
Before diving into troubleshooting steps, you’ll need to open the utility:
How to Open msconfig
| Method | Steps |
|---|---|
| Run Command | Press Windows + R, type msconfig, and press Enter |
| Start Menu Search | Type msconfig in the Start menu and click the result |
| Task Manager > File > Run | Open Task Manager, go to File > Run new task, type msconfig |
Step-by-Step: Using msconfig to Identify Crash Sources
The msconfig interface has several tabs, but for crash diagnostics, the General, Services, and Startup tabs are most relevant.
Step 1: Boot Into Selective Startup Mode
- Open msconfig.
- Under the General tab, choose Selective startup.
- Uncheck Load startup items, but keep Load system services checked.
- Click Apply, then OK and restart your PC.
Purpose: This disables all third-party startup programs, allowing you to test if the crash stems from these apps.
Step 2: Observe System Behavior
After restarting:
- If your crashes stop, a third-party startup item is likely the cause.
- If crashes continue, the issue may lie in a service or system process.
Make a note of the result before proceeding.
Step 3: Isolate Problematic Services
If startup programs weren’t the issue, the next step is to test services:
- Go to the Services tab in msconfig.
- Check Hide all Microsoft services at the bottom. This prevents disabling essential Windows processes.
- Click Disable all to turn off all non-Microsoft services.
- Click Apply, then OK and restart.
Result Interpretation:
| After Restart | Likely Cause |
|---|---|
| No crashes | One or more third-party services is faulty |
| Crashes persist | Hardware or core Windows issues may exist |
If crashes disappear, enable services in small groups (e.g., 3-5 at a time), restarting after each batch. This incremental re-enabling helps isolate the exact service causing issues.
Step 4: Investigate Startup Items (Windows 10/11 Users)
While msconfig no longer handles startup programs directly in newer Windows versions, it redirects you to Task Manager:
- In msconfig, click the Startup tab.
- Click Open Task Manager.
- Disable suspicious or non-essential programs one by one.
After each change, restart your computer and test its stability.
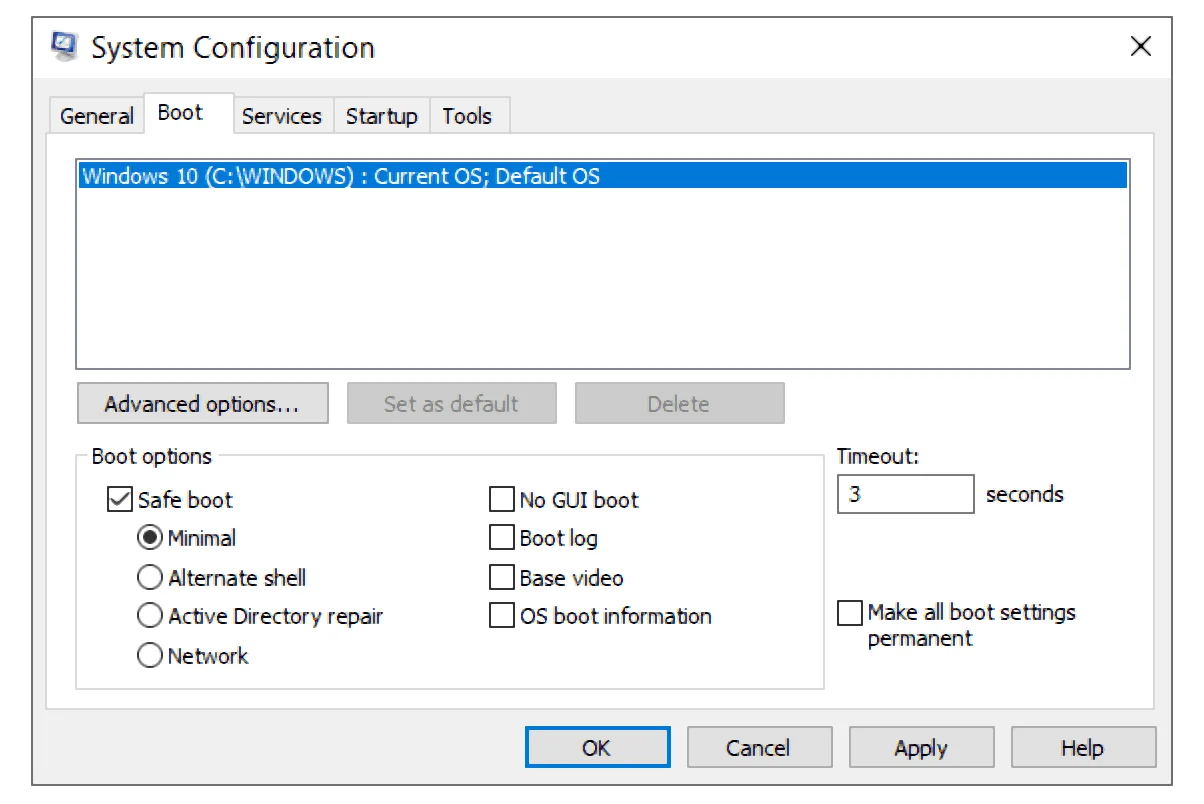
Step 5: Use Boot Options for Deep Diagnostics
In msconfig’s Boot tab, advanced options offer further diagnostic tools:
| Option | Function |
|---|---|
| Safe Boot | Starts Windows with only essential drivers and services |
| No GUI Boot | Disables the graphical boot screen, helpful for diagnosing display issues |
| Boot log | Creates a ntbtlog.txt file logging drivers loaded during startup |
| Base video | Boots using basic video drivers (useful for display driver conflicts) |
If you suspect graphics drivers are involved in crashes, select Base video or Safe Boot with networking, then update or roll back the drivers in Device Manager.
Practical Troubleshooting Workflow
To simplify, here’s a basic troubleshooting path:
| Step | Tool/Tab Used | Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Disable startup programs | General > Selective | Check if programs cause the crash |
| Disable non-Microsoft services | Services > Hide & Disable | Isolate problematic third-party services |
| Re-enable services in batches | Services tab | Pinpoint specific service causing failure |
| Use Safe Boot or Base Video | Boot tab | Identify driver-related or low-level system issues |
| Analyze boot logs | Boot > Boot log | Spot drivers or processes failing during startup |
What msconfig Can’t Do
While powerful, msconfig isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. It cannot:
- Identify failing hardware components
- Detect malware or rootkits
- Fix corrupted Windows installations
- Replace the need for tools like Event Viewer or Reliability Monitor
If msconfig helps narrow down the issue but can’t resolve it, consider using advanced tools like:
- Event Viewer (eventvwr.msc) for logs
- Driver Verifier (verifier.exe) to test drivers
- Windows Memory Diagnostic for RAM issues
- sfc /scannow or DISM for system file integrity
Tips to Maximize Effectiveness
- Keep a notebook or digital log of every change you make during testing.
- Always restart after each configuration change.
- Don’t disable Microsoft services unless you’re guided by an expert.
- Combine msconfig with System Restore to roll back if needed.
- Update all drivers after identifying and fixing the root cause.
System Configuration (msconfig) remains a versatile and accessible utility for tracking down sources of app or system crashes in Windows. While it doesn’t fix errors on its own, it enables a structured approach to isolate variables such as startup programs, background services, and driver conflicts. When used alongside other tools, msconfig can significantly reduce diagnostic time and help restore your system’s stability—without resorting to extreme solutions like reinstalling Windows.
For tech-savvy users and novices alike, understanding how to navigate msconfig effectively is a crucial skill in maintaining a smooth computing experience.